OpenVAS: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
You should be able to log in as ''admin'' using the initially generated password. After logging in, select ''User'' under the ''Administration'' menu and update your password (if desired). | You should be able to log in as ''admin'' using the initially generated password. After logging in, select ''User'' under the ''Administration'' menu and update your password (if desired). | ||
You should also be able to verify that the OpenVAS Command Line Interface (CLI) by running: | You should also be able to verify that the OpenVAS Command Line Interface (CLI) by running: | ||
Revision as of 09:58, 28 February 2018
Overview
The Open Vulnerability Assessment Scanner (OpenVAS) and Greenbone Security tools provide the following capabilities:
- Scan systems on your network looking for security risks.
- Manage and update the rule sets used for the scans.
- Produce reports based on the scans.
- Schedule periodic scans.
- Interact with the system via the command line, a desktop GUI interface, or a web based front end.
The OpenVAS project is a branch of the original Nessus software. More information can be found at http://www.openvas.com/.
The OpenVAS software package was included in the NST distribution starting with the 2.15.0 release.
![]() You should only setup your NST system for OpenVAS after performing a hard disk installation (within a virtual machine is OK). If you attempt to setup OpenVAS on a live boot you will likely run out of memory and lock your system.
You should only setup your NST system for OpenVAS after performing a hard disk installation (within a virtual machine is OK). If you attempt to setup OpenVAS on a live boot you will likely run out of memory and lock your system.
Quick Tip On Getting Started
- Define a target.
- Define a Task.
- Run Task.
NST 26 Setup
Getting OpenVAS (http://openvas.org) and Greenbone (https://www.greenbone.net/) set up and working on a NST 26 or Fedora 26 based system is a non-trivial task and involves some time (plan on 60 minutes). While the instructions below are based on a successful set up, due to the dynamic nature of all the packages and systems involved adjustments may need to be made in the future. Repeated use of the openvas-check-setup tool is highly recommended as you set up your system as it will not only indicate what is wrong, but will also provide useful instructions on what to do next to correct the issue.
Installation and Setup
NOTE: After NST 26 was release, the openvas packages were updated to version 9. The steps below assume that unix sockets (not TCP connections) will be used to communicate between the scanner (openvas-scanner service), manager (openvas-manager) and web interface (gsa-service). The only TCP port open should be 9443 after setup for the web interface. In order to accomplish this you will need to edit (comment) several lines in the /etc/sysconfig/openvas-* files.
Log into a terminal as root and make sure the following packages are installed (alien, nsis and texlive-collection-latexextra are optional, but you will be missing some functionality if you do not include them):
dnf install openvas-libraries openvas-scanner openvas-manager openvas-cli openvas-gsa gnutls-utils redis alien nsis texlive-collection-latexextra
Edit the file /etc/sysconfig/openvas-manager and comment out the TCP connection to the scanner and TCP listen configuration so that unix sockets are used by default:
#Manager listens on given address - by default manager listens on all addresses #MANAGER_LISTEN=--listen=127.0.0.1 #Manager listens on given port - by default 9390 #MANAGER_PORT=--port=9390 #Contact scanner on given address #SCANNER_LISTEN=--scanner-host=127.0.0.1 #Scanner listens on given port - by default 9391 #SCANNER_PORT=--scanner-port=9391
Edit the file /etc/sysconfig/openvas-gsa and comment out the TCP connection to the manager so that unix sockets are used by default:
#Contact manager on given address #MANAGER_LISTEN=--mlisten=127.0.0.1 #Manager listens on given port - by default 9390 #MANAGER_PORT=--mport=9390
Use the openvas-check-setup command as a diagnostic and guide during the installation process. We will be running this command a lot and it will report an ERROR until we complete the setup!
openvas-check-setup --v9
Edit the /etc/redis.conf file and make certain that the following two lines are uncommented (NOTE: We are not entirely certain that this step is required):
unixsocket /tmp/redis.sock unixsocketperm 700
Start and enable the redis service (restart if already running and you modified the configuration file):
systemctl restart redis.service systemctl enable redis.service # To enable at boot openvas-check-setup --v9
Update the security checks using the greenbone tools:
greenbone-nvt-sync greenbone-scapdata-sync greenbone-certdata-sync openvas-check-setup --v9
Start and enable the OpenVAS scanner service to initialize NVT cache:
systemctl start openvas-scanner.service systemctl enable openvas-scanner.service # To enable at boot # Wait for CPU to settle, eventually the following message should go # away from the openvas-check-setup - may take a long time: openvas-check-setup --v9
Rebuild the openvas manager database:
install -D -d -m 755 /var/lib/openvas/openvasmd/gnupg rm -f /var/lib/openvas/mgr/tasks.db openvasmd -f -v --rebuild openvas-check-setup --v9
Create a user account (admin in this example). Make sure you remember or copy/paste the password that is displayed (it will be a long string of random characters). Or, set it to a preferred password
openvasmd --create-user=admin --role=Admin # To change the password after creation, use: openvasmd --user=admin --new-password=PASSWORD openvas-check-setup --v9
Update the certificates:
openvas-manage-certs -a openvas-check-setup --v9
Start and enable the OpenVAS manager service:
systemctl start openvas-manager.service systemctl enable openvas-manager.service # To enable at boot openvas-check-setup --v9
Start and enable the Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA) service:
systemctl start openvas-gsa.service systemctl enable openvas-gsa.service # To enable at boot openvas-check-setup --v9
Accessing OpenVAS on an NST Probe
You should now be able to access the Greenbone Security Assistant at https://127.0.0.1:9443 (you can substitute the IP address of your NST system for the 127.0.0.1 if accessing remotely).
You should be able to log in as admin using the initially generated password. After logging in, select User under the Administration menu and update your password (if desired).
You should also be able to verify that the OpenVAS Command Line Interface (CLI) by running:
omp --ping omp -p 9390 --username=admin --password=YOUR_PASSWORD --xml="<help/>" ...
Refer to the http://openvas.org/ web site for instructions on using OpenVAS and the Greenbone Security Assistant.
NST 22 Setup
Installation and Setup
Log into a terminal as root and make sure the following packages are installed:
dnf install openvas-libraries openvas-scanner openvas-manager openvas-cli openvas-gsa gnutls-utils
Update the security checks using the openvas-nvt-sync tool:
openvas-nvt-sync
Edit the /etc/redis.conf file and make certain that the following two lines are uncommented (NOTE: We are not entirely certain that this step is required):
unixsocket /tmp/redis.sock unixsocketperm 777
Start and enable the redis service (restart if already running and you modified the configuration file):
systemctl restart redis.service systemctl enable redis.service
Start and enable the OpenVAS scanner and manager services:
systemctl start openvas-scanner.service systemctl enable openvas-scanner.service systemctl start openvas-manager.service systemctl enable openvas-manager.service
Create a client certificate:
openvas-mkcert-client -n -i
To test the connection, run (you can press Control-D to end the connection):
gnutls-cli --insecure -p 9391 127.0.0.1 --x509keyfile=/etc/pki/openvas/private/CA/clientkey.pem --x509certfile=/etc/pki/openvas/CA/clientcert.pem
Instruct OpenVAS to rebuild its database:
openvasmd --rebuild
Create a user account (admin in this example). Make sure you remember or copy/paste the password that is displayed (it will be a long string of random characters).
openvasmd --create-user=admin
Restart the OpenVAS manager service:
systemctl restart openvas-manager.service
Start and enable the Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA) service:
systemctl start openvas-gsa.service systemctl enable openvas-gsa.service
Accessing OpenVAS on an NST Probe
You should now be able to access the Greenbone Security Assistant at https://127.0.0.1:9443 (you can substitute the IP address of your NST system for the 127.0.0.1 if accessing remotely).
You should be able to log in as admin using the initially generated password. After logging in, select User under the Administration menu and update your password.
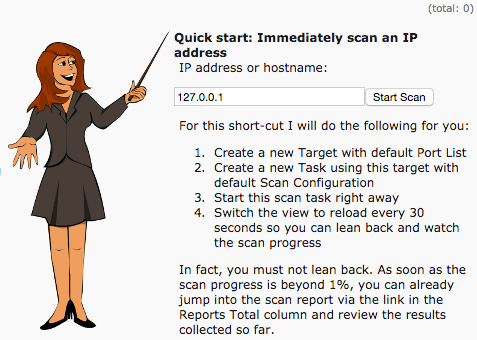
From the main page, you can perform a quick scan on the NST system itself by entering 127.0.0.1 and pressing the Start Scan button:
When the scan completes it may report a few medium severity issues related to the openvasmd process on port 9390.
You should also be able to verify that the OpenVAS Command Line Interface (CLI) by running:
omp --ping omp -p 9390 --username=admin --password=YOUR_PASSWORD --xml="<help/>" ...
Refer to the http://www.openvas.com/ web site for instructions on using OpenVAS and the Greenbone Security Assistant.
NST 16 and NST 18 Setup
Steps To Get OpenVAS Started With NST 16 and NST 18
- Add an OpenVAS client user (e.g., 'root') (Respond to all command prompts):
[root@dhcp132 ~]# openvas-adduser
- To synchronize OpenVAS security checks, use the openvas-nvt-sync command:
[root@dhcp132 ~]# openvas-nvt-sync
- Start the OpenVAS Scanner service. This will take minutes to hours to complete (at least the first time). If it takes too long, a failure will be reported, but the process will continue to run and parse the .nasl files out of the /var/lib/openvas/plugins directory. If you get hit with the timeout situtation, you can use the top' command to monitor the openvassd process :
[root@dhcp132 ~]# systemctl start openvas-scanner.service
- The OpenVAS Scanner service may take many minutes to start when initially loading all of the .nasl plugins found under the /var/lib/openvas/plugins directory. It may take so long that you may see a failure message reported in the previous step due to a time out. If this occurs, you can use the top command to monitor the load of the openvassd process and wait for the load the drop. Here's an example of a high load by the openvassd process:
top - 07:30:17 up 18:33, 3 users, load average: 1.50, 1.47, 1.25
Tasks: 142 total, 2 running, 140 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
Cpu0 : 7.6%us, 20.9%sy, 0.0%ni, 0.0%id, 0.8%wa, 68.9%hi, 1.8%si, 0.0%st
Mem: 1027908k total, 897168k used, 130740k free, 119148k buffers
Swap: 2064380k total, 612k used, 2063768k free, 480452k cached
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
27120 root 20 0 43092 35m 1832 S 17.9 3.6 2:04.78 openvassd
1 root 20 0 5688 3464 1952 S 0.5 0.3 0:08.17 systemd
306 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.1 0.0 0:00.88 jbd2/dm-1-8
4239 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.1 0.0 0:16.80 kworker/0:2
4262 root 20 0 57420 19m 9208 S 0.1 1.9 0:34.68 Xorg
- Before starting the openvas-manager (openvasmd) service, you need to initialize (rebuild) it's database the first time you set up your system. Run the following command to rebuild the database:
[root@dhcp132 ~]# openvasmd --rebuild
- Start the OpenVAS Manager service:
[root@dhcp132 ~]# systemctl start openvas-manager.service
- At this point both the OpenVAS Scanner (openvassd:9391) & Manager (openvasmd:9390) service should be started:
[root@dhcp132 ~]# netstat -tunap Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5900 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2024/vino-server tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:9390 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 27395/openvasmd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:9391 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 25093/openvassd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1391/httpd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1378/sshd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3001 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1382/ntop tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 11949/sshd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1391/httpd tcp 0 0 10.222.222.10:22 10.222.222.18:49240 ESTABLISHED 11949/sshd tcp 0 0 10.222.222.10:5900 10.222.222.18:53555 ESTABLISHED 2024/vino-server tcp 0 0 :::5900 :::* LISTEN 2024/vino-server tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1378/sshd tcp 0 0 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 11949/sshd udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:123 0.0.0.0:* 981/chronyd udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:323 0.0.0.0:* 981/chronyd udp 0 0 :::123 :::* 981/chronyd udp 0 0 :::323 :::* 981/chronyd [root@cayenne ~]# systemctl status openvas-scanner.service openvas-scanner.service - OpenVAS Scanner Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/openvas-scanner.service; disabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2013-05-10 20:43:42 EDT; 10h ago Main PID: 19509 (openvassd) CGroup: name=systemd:/system/openvas-scanner.service ├─10466 openvassd: serving 127.0.0.1 ├─10486 openvassd: serving 127.0.0.1 └─19509 openvassd: waiting for incoming connections May 10 20:41:53 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:42:03 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:42:14 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:42:26 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:42:40 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:42:54 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:43:10 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:43:28 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:43:42 cayenne openvassd[19439]: [120B blob data] May 10 20:43:42 cayenne systemd[1]: Started OpenVAS Scanner. [root@cayenne ~]# systemctl status openvas-manager.service openvas-manager.service - OpenVAS Manager Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/openvas-manager.service; disabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2013-05-10 20:54:37 EDT; 10h ago Main PID: 19571 (openvasmd) CGroup: name=systemd:/system/openvas-manager.service └─19571 /usr/sbin/openvasmd --port=9390 --slisten=127.0.0.1 --sport=9391 --otp May 10 20:54:37 cayenne systemd[1]: Starting OpenVAS Manager... May 10 20:54:37 cayenne systemd[1]: Started OpenVAS Manager. [root@cayenne ~]#
- Finally, from a Gnome Desktop start up the OpenVAS client (/usr/bin/openvas-client) and login as the user added in the first step:
Applications => System Tools => OpenVAS Client
NOTE: It takes a long time to load the initial rules when using openvas-client. The application may appear to hang and you may need to be patient for a few minutes as rules are loaded.
NOTE2: When openvas-client disconnects and exits, the openvassd process that was forked to serve it may not cleanly exit and consume 100% of a CPU. You can use the top command to identify and kill this process should it occur.
Accessing OpenVAS on an NST Probe
- From the NST WUI menu system (Web-Based Interface - WUI): Security => Active Scanners => Greenbone Security WUI (OpenVAS)
- From the Gnome or Fluxbox Desktop (X Window-Based Interface - GUI): Greenbone Security Desktop Tool
Steps To Get OpenVAS Started With NST 15
Command Line Setup
This section outlines the general procedure for setting up OpenVAS on a NST v2.15.0 system using the command line.
First Download/Update the OpenVAS Plugins
To install (or update if you've already installed the plugins at some point in the past), use the openvas-nvt-sync command. For example:
[root@dhcp132 ~]# openvas-nvt-sync ... Lots of output as rules are updated ... [root@dhcp132 ~]#
WARNING: Due not try this on a Live boot of the NST, as it writes a large amount of data to disk (which consumes RAM in a live boot).
The plugins for OpenVAS will be installed under the /var/lib/openvas/plugins directory. This directory won't exist until the initial plugins are installed using the openvas-nvt-sync command shown above. The following command shows how to get a count of the currently available plugins:
[root@dhcp132 ~]# ls /var/lib/openvas/plugins | wc -l 42962 [root@dhcp132 ~]#
Next Start The openvas-scanner Service
Starting the openvas-scanner (openvassd) service takes a long time. This occurs due to the loading and processing of all of the rules. When the service is started, it reads through all of the ASCII plugins and creates cached versions under the /var/cache/openvas directory. The first time you try and start the service, systemctl may time out and report that the service failed to start even though the openvassd process is still running and parsing rules. For example:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl start openvas-scanner.service Job failed. See system logs and 'systemctl status' for details. [root@cayenne ~]# ps -fC openvassd UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 3813 3812 48 13:30 ? 00:02:34 openvassd -q --port=9391 [root@cayenne ~]#
It takes a very long time for the initial loading and processing of the plugins. You can try to peek at what plugins are currently being loaded (to assure yourself that progress is being made) using the lsof command (this doesn't always work and depends a bit on the start of the openvassd process):
[root@cayenne ~]# lsof | grep /var/lib/openvas/plugins openvassd 12858 root cwd 4r REG 253,1 2635 21050 /var/lib/openvas/plugins/plugins/gb_MDaemon_39857.nasl [root@cayenne ~]#
If you run the top command while the openvassd is processing the plugins, you should see the openvassd consuming a substantial amount of CPU.
Eventually the openvassd process will complete it's loading phase and enter into a state where it is ready to accept incoming connections. You can use the ps command to check for this.
[root@dcayenne ~]# ps -fC openvassd UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 24529 1 0 07:13 ? 00:00:00 openvassd: waiting for incoming [root@dcayenne ~]#
The systemctl command can also be used to verify that the openvassd process is ready for incoming connections:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl status openvas-scanner.service openvas-scanner.service - LSB: start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|reloadplugins OpenVAS Scanner Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-scanner) Active: failed since Wed, 15 Jun 2011 07:10:23 -0400; 7min ago Process: 2164 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-scanner start (code=killed, signal=TERM) CGroup: name=systemd:/system/openvas-scanner.service └ 24529 openvassd: waiting for incoming connections [root@cayenne ~]#
You may notice that systemctl reports the service in a failed state even though the openvassd daemon is running and accepting connections. You should be able to clear this failed state indicator by restarting the service.
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl restart openvas-scanner.service [root@cayenne ~]# systemctl status openvas-scanner.service openvas-scanner.service - LSB: start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|reloadplugins OpenVAS Scanner Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-scanner) Active: active (running) since Sat, 16 Jul 2011 13:44:52 -0400; 1min 6s ago Process: 27198 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-scanner start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 27193 (openvassd) CGroup: name=systemd:/system/openvas-scanner.service └ 27193 openvassd: waiting for incoming connections [root@cayenne ~]# [root@cayenne ~]#
To enable the openvas-scanner (openvassd) service at boot time, run the following command:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl enable openvas-scanner.service openvas-scanner.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig. Executing /sbin/chkconfig openvas-scanner on [root@cayenne ~]#
Next Start The openvas-manager Service
Before starting the openvas-manager (openvasmd) service, you need to initialize (rebuild) it's database the first time you set up your system. Run the following command to rebuild the database:
[root@cayenne ~]# openvasmd --rebuild [root@cayenne ~]#
Once the database has been setup, you can start the service in the following manner:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl start openvas-manager.service [root@cayenne ~]# systemctl status openvas-manager.service openvas-manager.service - LSB: start|stop|status|restart|condrestart OpenVAS Manager Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-manager) Active: active (running) since Sat, 16 Jul 2011 13:56:41 -0400; 5s ago Process: 27445 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-manager start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 27450 (openvasmd) CGroup: name=systemd:/system/openvas-manager.service └ 27450 openvasmd --port=9390 --slisten=127.0.0.1 --sport=... [root@cayenne ~]#
To enable the openvas-manager (openvasmd) service at boot time, run the following command:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl enable openvas-manager.service openvas-manager.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig. Executing /sbin/chkconfig openvas-manager on [root@cayenne ~]#
Next Start The openvas-administrator Service
Before starting the openvas-administrator (openvasad) service, you need to add a administrative user. The following demonstrates how to add a root user (you can choose any name you prefer):
[root@cayenne ~]# openvasad -c add_user -n root --role=Admin Enter password: ad main:MESSAGE:23822:2011-06-15 07h54.32 EDT: No rules file provided, the new user will have no restrictions. ad main:MESSAGE:23822:2011-06-15 07h54.32 EDT: User root has been successfully created. [root@cayenne ~]#
Once a administrative user has been added, you should be able to start the service as shown below
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl start openvas-administrator.service [root@cayenne ~]# systemctl status openvas-administrator.service openvas-administrator.service - LSB: start|stop|status|restart|condrestart OpenVAS Manager Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-administrator) Active: active (running) since Sat, 16 Jul 2011 13:59:17 -0400; 3s ago Process: 27475 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/openvas-administrator start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 27480 (openvasad) CGroup: name=systemd:/system/openvas-administrator.service └ 27480 openvasad --port=9393 [root@cayenne ~]#
To enable the openvas-administrator (openvasad) service at boot time, run the following command:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl enable openvas-administrator.service openvas-administrator.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig. Executing /sbin/chkconfig openvas-administrator on [root@cayenne ~]#
Next Start The gsad Service
Once the OpenVAS services are set up and running, you should be able to start the Greenbone Security Assistant service as follows:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl start gsad.service [root@cayenne ~]# systemctl status gsad.service gsad.service - LSB: This starts and stops the Greenbone Security Assistant. Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/gsad) Active: active (running) since Sat, 16 Jul 2011 14:14:30 -0400; 4s ago Process: 27880 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/gsad start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 27886 (gsad) CGroup: name=systemd:/system/gsad.service └ 27886 /usr/sbin/gsad --port=9392 --alisten=127.0.0.1 --a... [root@cayenne ~]#
To enable the gsad service at boot time, run the following command:
[root@cayenne ~]# systemctl enable gsad.service gsad.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig. Executing /sbin/chkconfig gsad on [root@cayenne ~]#
Finally Verify Your Setup Using openvas-check-setup
After you have all of the services set up and running, you can use the openvas-check-setup command to perform a sanity check on your system to verify that it has been setup correctly.
[root@cayenne ~]# openvas-check-setup
... Lots of output as various checks are performed.
If not all OK, then a SUGGESTION should appear ...
It seems like your OpenVAS-4 installation is OK.
If you think it is not OK, please report your observation
and help us to improve this check routine:
http://lists.wald.intevation.org/mailman/listinfo/openvas-discuss
Please attach the log-file (/tmp/openvas-check-setup.log) to help us analyze the problem.
[root@cayenne ~]#