HowTo Geolocate ntop Data: Difference between revisions
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
This '''HowTo''' explains the procedure for setting up an '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' session and producing on demand '''host''' geolocations rendered on either a '''Mercator World Map''' projection or on a '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language KML]''' '''Earth Browser''' such as '''[http://earth.google.com Google Earth]''', '''[http://maps.google.com Google Maps]''' or '''[http://edu.kde.org/marble Marble]'''. | This '''HowTo''' explains the procedure for setting up an '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' session and producing on demand '''host''' geolocations rendered on either a '''Mercator World Map''' projection or on a '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language KML]''' '''Earth Browser''' such as '''[http://earth.google.com Google Earth]''', '''[http://maps.google.com Google Maps]''' or '''[http://edu.kde.org/marble Marble]'''. | ||
One of the goals of the NST WUI is to provide a web-based front-end to numerous open source network security applications. Trying to build out a web-based interface that has a common look-and-feel across the vast spectrum of applications is a daunting task. Before diving into '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' | One of the goals of the NST WUI is to provide a web-based front-end to numerous open source network security applications. Trying to build out a web-based interface that has a common look-and-feel across the vast spectrum of applications is a daunting task. Before diving into producing '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' '''Hosts Geolocations''', one needs to understand best practices on how to setup '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' session as a '''Host''' data source collector. This first involves getting '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' up and running using the NST WUI interface and then secondly filtering how much data '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' is configured to collect using the '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' administrative controls. | ||
The input and selections fields for setting up an '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' session using the NST WUI interface will be explained so that it will become routine across NST systems. | The input and selections fields for setting up an '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' session using the NST WUI interface will be explained so that it will become routine across NST systems. | ||
Revision as of 06:03, 15 September 2010
Overview
This HowTo explains the procedure for setting up an ntop session and producing on demand host geolocations rendered on either a Mercator World Map projection or on a KML Earth Browser such as Google Earth, Google Maps or Marble.
One of the goals of the NST WUI is to provide a web-based front-end to numerous open source network security applications. Trying to build out a web-based interface that has a common look-and-feel across the vast spectrum of applications is a daunting task. Before diving into producing ntop Hosts Geolocations, one needs to understand best practices on how to setup ntop session as a Host data source collector. This first involves getting ntop up and running using the NST WUI interface and then secondly filtering how much data ntop is configured to collect using the ntop administrative controls.
The input and selections fields for setting up an ntop session using the NST WUI interface will be explained so that it will become routine across NST systems.
ntop Setup
This section describes how to setup an ntop session using the NST WUI.
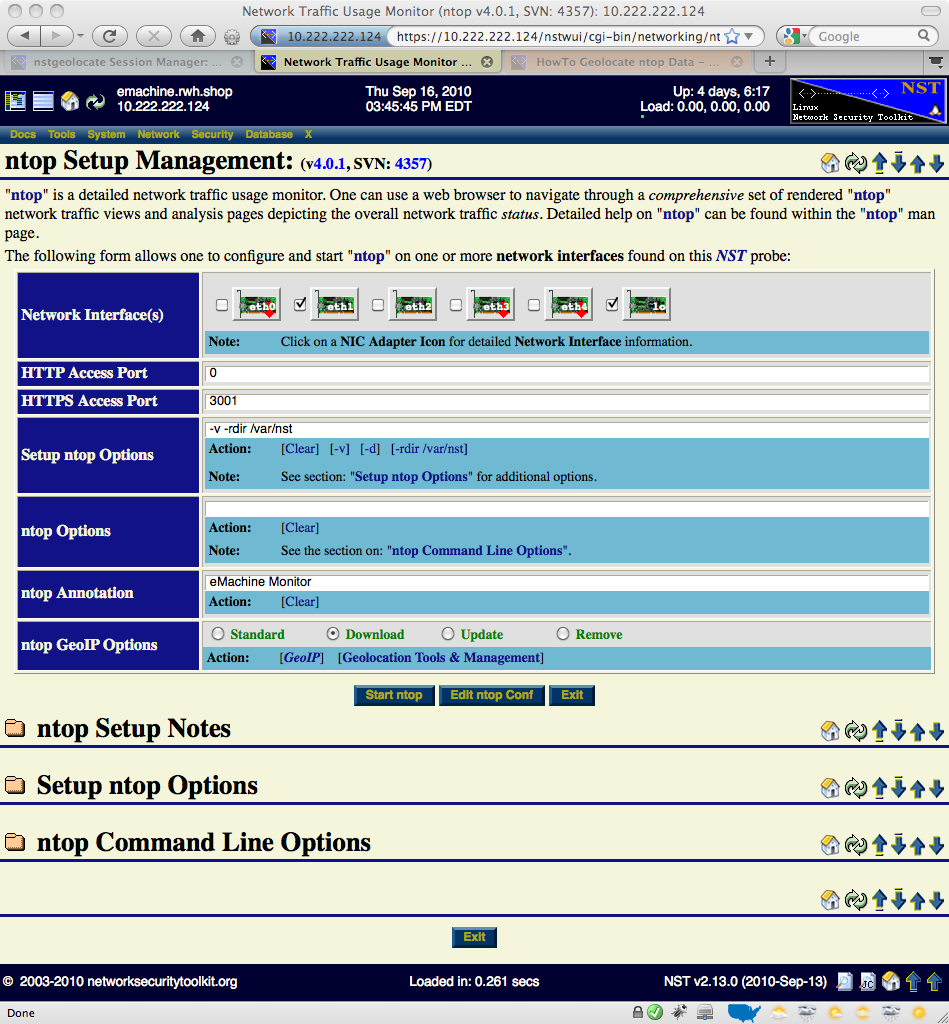
The image above depicts the NST WUI ntop setup management page. Use the following steps to setup an ntop session.
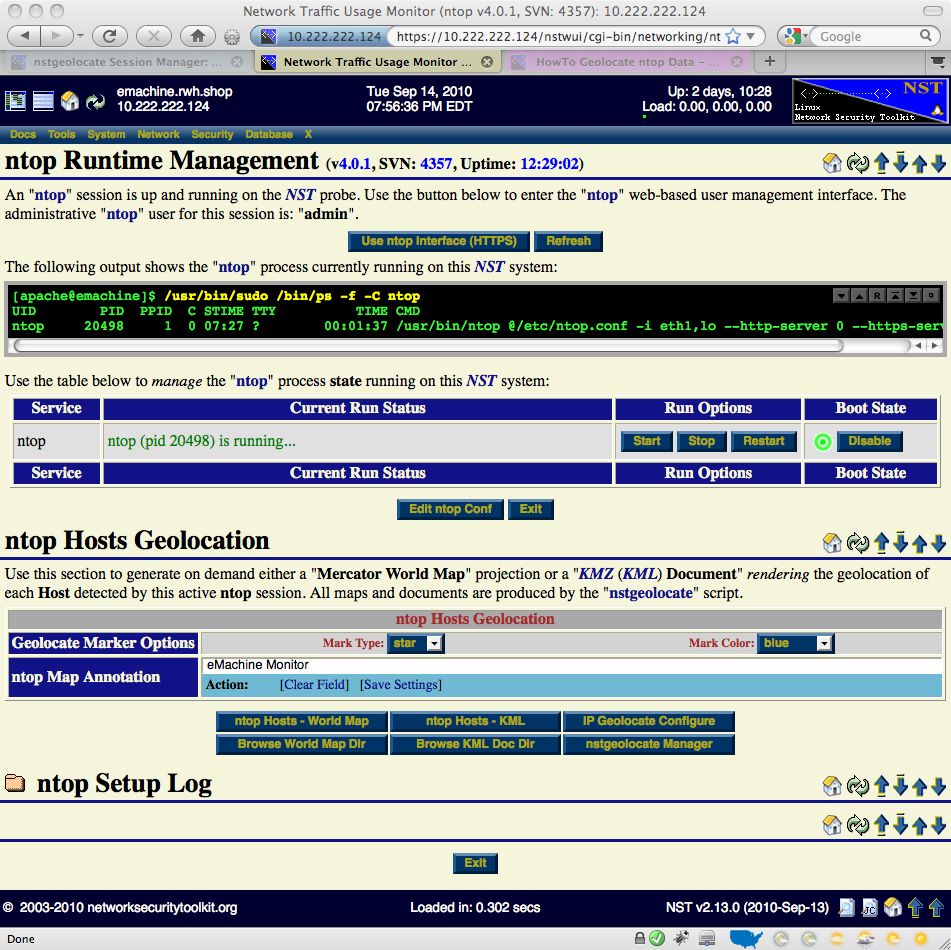
ntop Runtime Management
Once an ntop session is up and running, one can now produce on demand host geolocations.